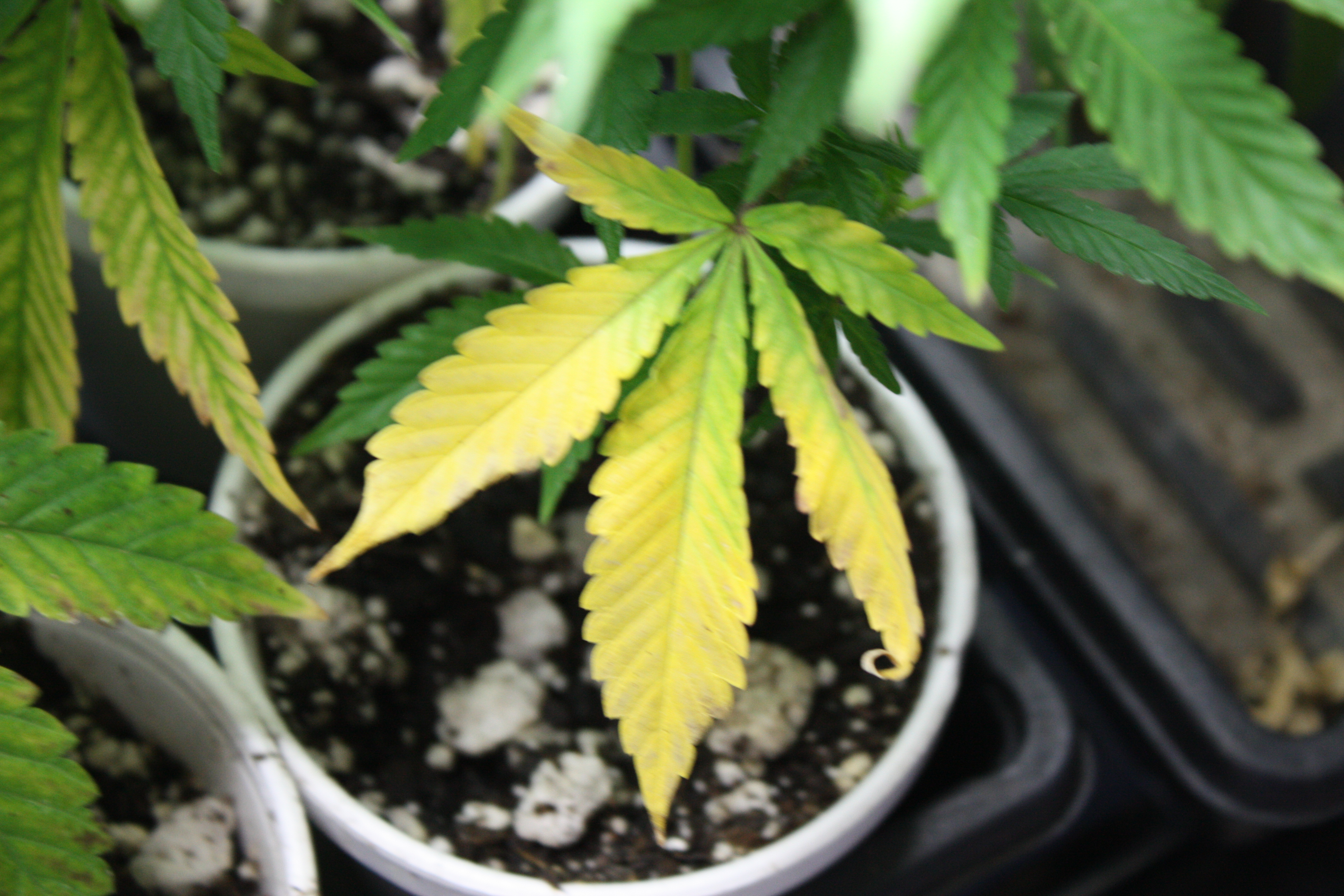
Welcome to the not-so-green side of Cannabis plant deficiencies—where nutrient deficiencies can turn your grow into a guessing game. We’re here to help both new and seasoned growers navigate these issues confidently. Nutrient deficiencies can stunt growth, reduce yields, and even kill plants if not addressed. But don’t worry—understanding cannabis nutrients is easier than it seems.
In this guide, we’ll identify common nutrient deficiencies, explain the role of each nutrient, and provide solutions to keep your plants healthy. This isn’t just about growing weed; it’s about cultivating a thriving ecosystem. Join the Bud Wize community as we turn challenges into opportunities and elevate your cannabis cultivation journey.
Table of Contents
The Importance of Nutrient Balance in Cannabis Cultivation
Getting the right nutrient balance is essential for a successful cannabis grow. Cannabis plants, like intricate little green machines, need a specific mix of nutrients to thrive—whether it’s growing tall, producing abundant buds, or staying healthy. Each nutrient plays a crucial role, from maintaining structural integrity to driving metabolic processes. Achieving this balance isn’t just beneficial; it’s critical for the plant’s overall health and productivity.
Nutrients: The Building Blocks of Plant Health
- Macronutrients (NPK): Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K) are the primary nutrients that cannabis plants consume in large quantities. They support fundamental aspects of plant growth such as leaf development, root growth, and flower production.
- Secondary Nutrients: Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), and Sulfur (S) are consumed in smaller amounts but are no less important. They play crucial roles in cell wall structure, photosynthesis, and enzyme function.
- Micronutrients: Iron (Fe), Zinc (Zn), Manganese (Mn), Boron (B), and others are needed in trace amounts. Despite their small required quantities, their impact on plant health and development is significant.
Consequences of Nutrient Imbalance
- Deficiency Symptoms: Lack of any nutrient can lead to specific symptoms. For example, nitrogen deficiency results in yellowing leaves, while potassium deficiency can cause leaf edges to appear burnt. Each symptom provides clues to the missing nutrient.
- Toxicity Symptoms: Just as deficiency is harmful, an excess of nutrients can lead to toxicity. Symptoms of nutrient burn include brown, crispy leaf edges, and stunted growth, which can be just as detrimental as deficiencies.
- Impact on Yield and Quality: Beyond aesthetics, nutrient imbalances affect the yield and quality of cannabis. Deficiencies can lead to reduced bud size and potency, while toxicities can damage plants to the point of harvest being infeasible.
Achieving Nutrient Balance
- Soil Testing: Regular soil testing can provide insights into the nutrient composition and pH level of your growing medium, allowing for precise adjustments.
- pH Management: Nutrient availability is closely tied to soil pH. Ensuring the pH is within the optimal range for cannabis (usually between 6.0 and 7.0 for soil grows) is essential for nutrient uptake.
- Careful Fertilization: Applying the right type and amount of fertilizer based on plant stage and soil test results can prevent imbalances. It’s often better to under-fertilize and adjust as needed than to overdo it and risk toxicity.
Understanding and managing nutrient balance is a dynamic process, requiring observation, knowledge, and sometimes, a bit of trial and error. By recognizing the importance of each nutrient and how to maintain its balance, you can ensure your cannabis plants are healthy, vibrant, and productive.

Dive into Nitrogen (N) Deficiency Details
Nitrogen is fundamental to plant growth, being a key component of chlorophyll, amino acids, and nucleic acids. It plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. A nitrogen deficiency can severely impact a cannabis plant’s growth and overall health.
Symptoms of Nitrogen Deficiency
- Older Leaves Turn Yellow: One of the first signs of nitrogen deficiency is the yellowing of older, lower leaves. This occurs because nitrogen is a mobile nutrient within the plant, meaning the plant can move it from older leaves to newer ones when in short supply.
- Stunted Growth: Nitrogen is vital for plant growth. A deficiency can lead to slowed or stunted growth as the plant lacks the necessary components for cell growth and division.
- Weak Stems: With inadequate nitrogen, stems may become thin and weak, struggling to support the plant’s weight.
- Overall Reduced Vigor: The plant may appear generally unhealthy, with reduced vitality and slower development rates.
Solutions for Nitrogen Deficiency
Correcting a nitrogen deficiency requires careful supplementation to avoid overcompensation and nutrient burn.
- Organic Amendments:
- Blood Meal: A fast-acting source of nitrogen. It can be mixed into the soil or used as a top dressing.
- Fish Emulsion: Another rapid source of nitrogen, fish emulsion is diluted with water and applied directly to the soil or as a foliar spray.
- Inorganic Fertilizers:
- Look for a fertilizer with a higher N (nitrogen) value in the N-P-K ratio (e.g., 20-10-10). This indicates a higher nitrogen content relative to phosphorus and potassium.
- Adjusting Feeding Schedule:
- If using a liquid nutrient solution, you can adjust the mix to increase the nitrogen content during the next few feedings.
Best Practices
- Gradual Adjustment: Start with a lower dose of nitrogen supplement to avoid shock or nutrient burn. Gradually increase as needed based on the plant’s response.
- Monitor pH: Ensure the soil or growing medium’s pH is within the optimal range for nutrient uptake (6.0 to 7.0 for soil grows). Nitrogen uptake can be hindered by pH imbalances.
- Observe Changes: After supplementation, watch for signs of improvement or further issues. It can take a week or more for the plant to recover fully.
Spotting the signs of nitrogen deficiency early and knowing how to fix it can keep your cannabis plants healthy and thriving all season long. The trick with cannabis plant deficiencies isn’t just about jumping in to correct them when they pop up; it’s about staying ahead of the game with regular checks and balanced nutrition. That way, you can prevent issues before they even start, keeping your grow on point and your plants happy.

Explore Phosphorus (P) Deficiency Solutions
Phosphorus is a big deal when it comes to keeping your cannabis plants running smoothly. It’s all about energy transfer, photosynthesis, and whipping up those nucleic acids and ATP. This nutrient really shines during the flowering stage, helping buds bulk up and roots dig deep. Spotting and fixing phosphorus deficiencies is crucial for a healthy, thriving cannabis garden that produces the goods.
Symptoms of Phosphorus Deficiency
- Darkening of Leaves: One of the first signs is a dark green or purplish tint on the leaves, especially noticeable on the underside and along the edges.
- Poor Bud Development: Phosphorus is essential for flower formation. Deficiency can lead to sparse or poor-quality bud development.
- Weak Root System: Phosphorus supports strong root growth. A deficiency can result in a fragile root system, further affecting the plant’s overall health and nutrient uptake.
- Stunted Growth: Similar to nitrogen, a lack of phosphorus can slow down the growth rate of the cannabis plant.
Solutions for Phosphorus Deficiency
Correcting phosphorus deficiency requires the addition of phosphorus-rich nutrients or amendments to the soil.
- Organic Amendments:
- Bone Meal: A slow-release source of phosphorus, bone meal is ideal for soil amendments, gradually improving phosphorus levels.
- Bat Guano: Depending on the source, bat guano can be high in phosphorus, making it a good organic option for boosting phosphorus levels.
- Inorganic Fertilizers:
- Look for fertilizers with a higher P (phosphorus) value in the N-P-K ratio. A bloom-specific fertilizer often has increased phosphorus content to support flower development.
- Liquid Phosphorus Supplements:
- There are liquid forms of phosphorus supplements available that can be directly added to your watering routine for a quicker response than solid amendments.
Best Practices
- Soil Testing: Before adding phosphorus, test your soil to ensure that phosphorus is indeed deficient and to avoid over-supplementation.
- pH Management: Ensure the soil pH is within the optimal range (6.0 to 7.0 for soil grows) for phosphorus uptake. Phosphorus availability decreases in highly acidic or alkaline soils.
- Gradual Addition: Start with smaller amounts of phosphorus supplements and adjust based on the plant’s response to avoid phosphorus toxicity.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Once you’ve tackled phosphorus deficiency, keep an eye on your cannabis plants to see if they’re bouncing back. Look for stronger roots, better bud development, and healthier leaf color—all signs that you’ve nailed the fix. Knowing how to spot and handle phosphorus deficiencies gives you the power to keep your cannabis plants thriving, maximizing both their growth and yield potential.

Learn about Potassium (K) Deficiency Corrections
Potassium is a game-changer for cannabis plants, playing a key role in water uptake, enzyme activation, and the production of proteins and starches. It also regulates the stomata, which means it affects photosynthesis and how plants manage water loss. When it comes to growing cannabis, a potassium deficiency can mess with plant health, stunt growth, and make your plants less resilient overall.
Symptoms of Potassium Deficiency
- Yellowing or Browning Leaf Edges: Leaves may display yellow or brown edges that appear burnt, a hallmark of potassium deficiency.
- Weak Stems and Slow Growth: Potassium is vital for strong cellular walls and overall plant vigor, making its deficiency apparent in weak stems and stunted growth.
- Leaf Wilting: Despite adequate water, leaves might wilt due to poor water regulation within the plant.
- Spotted or Patchy Leaves: In some cases, leaves may develop dark spots or patches as a symptom of potassium deficiency.
Solutions for Potassium Deficiency
Addressing potassium deficiency involves incorporating potassium-rich supplements or fertilizers into your cannabis plant care regimen.
- Organic Amendments:
- Wood Ash: Contains a significant amount of potassium and can be mixed into the soil. However, it also affects soil pH, so use it cautiously.
- Kelp Meal: A slower-release, organic source of potassium that also adds other beneficial micronutrients to the soil.
- Inorganic Fertilizers:
- Fertilizers with a higher K (potassium) value in the N-P-K ratio are effective for quick supplementation. Look for “bloom” formulas, which typically have increased potassium for flower support.
- Potassium Sulfate: A soluble potassium source that can be applied directly to the soil or used as a foliar spray for rapid uptake.
Best Practices
- Soil Testing: Conduct soil tests to confirm potassium deficiency before supplementation to avoid over-application.
- pH Management: Optimal nutrient uptake, including potassium, occurs when soil pH is within the 6.0 to 7.0 range. Adjust soil pH if necessary.
- Careful Application: Start with lower doses of potassium supplements and monitor plant response. Excessive potassium can interfere with the uptake of other nutrients, like magnesium and calcium.
Monitoring and Adjustment
After addressing potassium deficiency, keep a close watch on your plants for signs of recovery. Look for the browning on leaf edges to stop spreading and for the plants to perk up in general. Remember, recovery from nutrient deficiencies isn’t instant—damaged leaves won’t heal, but new growth should show that the nutrient balance is back on track.
Potassium is essential for the overall health and productivity of your cannabis plants. Knowing how to spot and fix potassium deficiencies is key to maximizing growth, boosting yield, and helping your plants withstand stressors.

Understand Calcium (Ca) Deficiency Remedies
Calcium is a must-have for cannabis plants, crucial for building strong cell walls, promoting root growth, and ensuring overall plant stability and health. It’s also vital for various enzymatic processes and helps the plant handle heat stress. Without enough calcium, your cannabis plants can face serious health problems, stunted growth, and lower yields.
Symptoms of Calcium Deficiency
- New Growth Issues: Young leaves or new shoots may appear twisted or distorted, with irregular shapes and crinkled margins.
- Necrotic Spots: Small, localized dead spots may appear on new leaves, indicating cell death due to insufficient calcium.
- Stunted Growth: Calcium is critical for cell division and growth. A deficiency can significantly slow down plant growth.
- Weak Root System: The root system may become underdeveloped or weak, impacting the plant’s ability to uptake water and nutrients.
Solutions for Calcium Deficiency
Correcting a calcium deficiency involves supplementing the plant with calcium through various means.
- Dolomitic Lime: Adding dolomitic lime to the soil can help increase calcium levels and adjust pH towards a more neutral range, enhancing nutrient availability.
- Gypsum (Calcium Sulfate): Gypsum is another soil amendment that provides calcium without significantly altering soil pH.
- Calcium-Magnesium Supplements (Cal-Mag): These supplements provide both calcium and magnesium, which often need replenishment together, especially in hydroponic systems or coco coir growing mediums.
Best Practices
- Water Quality Check: Ensure your water source does not have high levels of sodium or other elements that can interfere with calcium uptake.
- Monitor pH Levels: Calcium uptake is optimal in soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0. Adjust soil pH if it falls outside this range.
- Balanced Nutrient Solution: In hydroponic setups, regularly check and maintain the nutrient solution’s balance to prevent calcium lockout due to excess levels of other nutrients.
Monitoring and Maintenance
After addressing a calcium deficiency in your cannabis plants, monitor them closely for signs of recovery. Focus on new growth, as existing damage is typically irreversible. Improvements in leaf structure, overall plant vigor, and root health are good indicators that the issue has been resolved. Regularly checking and adjusting growing conditions can help prevent future deficiencies.
Understanding the importance of calcium and knowing how to correct its deficiency can significantly impact your plants’ health and productivity. Proper calcium levels support strong plant development and help maximize the effectiveness of your cultivation efforts.

Address Magnesium (Mg) Deficiency Solutions
Magnesium is crucial for cannabis plant health and development. It’s the central atom in the chlorophyll molecule, making it essential for photosynthesis. Additionally, magnesium helps activate enzymes and assists in the movement of phosphorus within the plant. When there’s a magnesium deficiency, it can severely impact the plant’s ability to produce energy and synthesize proteins, leading to significant growth issues
Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
- Interveinal Chlorosis: Older leaves, particularly those lower on the plant, exhibit yellowing between the veins while the veins themselves remain green.
- Leaf Curl and Drop: Affected leaves may curl upward and eventually drop off the plant.
- Reddish or Purple Tints: In some cases, the leaves may develop reddish or purple hues due to the breakdown of sugars that accumulate in the leaves.
- Reduced Growth and Flowering: Magnesium deficiency can slow down the growth and flowering of cannabis plants, affecting yield and quality.
Solutions for Magnesium Deficiency
Correcting a magnesium deficiency involves supplementing with magnesium in an accessible form for the plants.
- Epsom Salts (Magnesium Sulfate):
- Soil Application: Dissolve Epsom salts in water and apply to the soil. This method slowly increases magnesium levels without drastically altering soil pH.
- Foliar Spray: A solution of Epsom salts can be sprayed directly onto the leaves for quicker absorption by the plants.
- Magnesium-Rich Fertilizers:
- Fertilizers labeled with a higher magnesium content or those specifically designed to address magnesium deficiencies can be effective.
- Dolomitic Lime:
- For soils that are also deficient in calcium, dolomitic lime provides both calcium and magnesium, improving overall soil health and nutrient balance.
Best Practices
- Soil Testing: Conduct a soil test to confirm magnesium deficiency and to understand the soil’s overall nutrient profile and pH level.
- pH Adjustment: Magnesium availability is affected by soil pH. Ensure the pH is within the optimal range for cannabis (6.0 to 7.0 for soil, 5.5 to 6.5 for hydroponics).
- Careful Application: Start with lower doses of magnesium supplements to avoid overcompensation, which could lead to other nutrient imbalances.
Monitoring and Adjustment
After adding magnesium, keep an eye on your plants for signs of recovery. Focus on new growth, as the damaged leaves likely won’t bounce back. Look for a return of green in the leaves and a boost in the plant’s overall vigor and health.
Tackling magnesium deficiency quickly can prevent major setbacks in your cannabis plants’ growth and yield, helping you maintain a healthy and productive cultivation journey (I wonder how many times I used the word tackle).

Correct Sulfur (S) Deficiency Practices
Sulfur is a crucial element in plant nutrition, integral to the synthesis of essential amino acids and vitamins. It also plays a vital role in chlorophyll formation and photosynthesis. Sulfur deficiency in cannabis can lead to reduced growth and delayed maturity, making its early detection and correction vital for healthy plant development.
Symptoms of Sulfur Deficiency
- Young Leaves Turning Pale Yellow: Unlike most other nutrient deficiencies, sulfur deficiency first appears in the younger leaves at the top of the plant because sulfur is not mobile within the plant.
- Stunted Growth: Plants may exhibit overall reduced growth rates due to insufficient sulfur.
- Delayed Maturity: A lack of sulfur can slow down the development process, affecting the flowering and maturation stages.
Solutions for Sulfur Deficiency
Addressing sulfur deficiency involves supplementing the plant’s sulfur intake, which can be achieved through various means.
- Epsom Salts (Magnesium Sulfate):
- Epsom salts not only provide magnesium but also supply sulfur. It can be dissolved in water and used both as a soil drench and foliar spray.
- Gypsum (Calcium Sulfate):
- Gypsum is another effective amendment for adding sulfur (and calcium) to the soil without significantly altering the soil pH.
- Sulfur-Containing Fertilizers:
- Fertilizers that contain sulfate forms of nutrients can help address sulfur deficiency while also contributing to the plant’s overall nutrient needs.
Best Practices
- Soil Testing: Before applying sulfur supplements, it’s recommended to perform a soil test to confirm sulfur deficiency and to check for other potential nutrient imbalances.
- pH Considerations: Sulfur applications can slightly lower soil pH over time, so monitor soil pH if making repeated sulfur applications, especially in soils already on the acidic side.
- Moderation is Key: Sulfur is needed in relatively small amounts, so it’s important to apply it judiciously to avoid excess, which can be harmful to the plant.
Monitoring and Maintenance
After addressing a sulfur deficiency, monitor your cannabis plants closely for signs of recovery, focusing particularly on new growth. Look for younger leaves returning to a healthy green color and an overall improvement in the plant’s growth rate.
Timely and accurate correction of sulfur deficiency is crucial for maintaining the health and productivity of your cannabis plants. Ensuring a balanced sulfur supply supports robust plant growth and optimal development. By staying vigilant and making necessary adjustments, growers can prevent future deficiencies and promote a thriving cultivation environment.

Explore Solutions for Iron (Fe) Deficiency
Iron is a vital micronutrient for cannabis plants, essential for chlorophyll synthesis, and acting as a catalyst for energy transfer. It’s key to photosynthesis and numerous metabolic pathways. An iron deficiency often shows up as interveinal chlorosis (yellowing between the veins) in young leaves, which can seriously harm plant health and reduce yields if not quickly corrected.
Symptoms of Iron Deficiency
- Interveinal Chlorosis in Young Leaves: The most distinctive symptom of iron deficiency is the yellowing of young leaves while the veins remain dark green. This symptom is usually observed in the newest growth at the top of the plant.
- Stunted Growth: As with many nutrient deficiencies, iron deficiency can lead to slowed or stunted growth due to impaired photosynthesis and energy transfer.
- Leaf Drop: In severe cases, affected leaves may become so deficient that they fall off the plant.
Solutions for Iron Deficiency
The correction of iron deficiency involves ensuring that plants have access to bioavailable iron, which can be influenced by several factors, including soil pH and moisture levels.
- Chelated Iron Supplements:
- Chelated iron is a form of iron that is readily available for plant uptake, even in higher pH soils. It can be added to the soil or used as a foliar spray for quick absorption.
- Adjusting Soil pH:
- Iron becomes less available to plants as soil pH increases above 6.5. Lowering the soil pH can help make iron more accessible to plants. This can be achieved through the addition of sulfur or a soil acidifier.
- Iron-Rich Fertilizers:
- Some fertilizers are formulated with higher levels of iron or include iron as part of a micronutrient blend, ideal for correcting or preventing deficiencies like Iron-Tone.
Best Practices
- Confirm Deficiency Through Testing: Before adding iron supplements, ensure that iron deficiency is the actual problem, as symptoms can sometimes mimic those of other issues.
- Careful Application: When using iron supplements, especially chelates, follow the manufacturer’s instructions to avoid over-application, which can lead to toxicity.
- Monitor and Adjust: After treatment, monitor the plant’s response. Improvement in newer leaves should be noticeable within a few weeks if iron deficiency was the issue.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Recovery from iron deficiency can be seen in the appearance of green, healthy leaves in the new growth areas of the plant. It’s crucial to keep monitoring the plant for these signs of recovery and to adjust your care practices to prevent the deficiency from returning.
By promptly identifying and correcting iron deficiency, you ensure that your cannabis plants can continue photosynthesizing effectively, maintain healthy growth, and achieve high yields.

Review Zinc (Zn) Deficiency Remedies
Zinc is an essential micronutrient for cannabis plants, playing a key role in various physiological processes like enzyme function, protein synthesis, and growth hormone production. It’s particularly crucial for chlorophyll formation and carbohydrate metabolism. A zinc deficiency can cause serious issues, including stunted growth and malformed leaves, severely affecting overall plant health and development.
Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
- Reduced Leaf Size: One of the hallmark symptoms of zinc deficiency is noticeably smaller leaves than normal.
- Leaf Discoloration: Young leaves may exhibit interveinal chlorosis, showing a light green color between darker green veins.
- Shortened Stem Length: Internodes (the spaces between leaves on the stem) may become shorter, giving the plant a stunted appearance.
- Leaf Malformation: New leaves might emerge twisted or distorted, and older leaves can develop a rough texture.
Solutions for Zinc Deficiency
Correcting a zinc deficiency requires ensuring that plants have access to adequate zinc in a form they can absorb.
- Zinc Supplements:
- Applying a zinc supplement, such as zinc sulfate, can quickly address zinc deficiency. It can be applied directly to the soil or used as a foliar spray for rapid uptake.
- Chelated Zinc:
- Like other chelated minerals, chelated zinc like the Greenway Biotech Brand is designed to be easily absorbed by plants, reducing the risk of precipitation and improving bioavailability, especially in alkaline soils.
- Balanced Micronutrient Fertilizers:
- Fertilizers that include a balanced spectrum of micronutrients, including zinc, can help prevent deficiencies and ensure overall plant health.
Best Practices
- Soil pH Adjustment: Zinc availability decreases in alkaline soils. Lowering soil pH can help make zinc more accessible to your plants.
- Careful Dosage: Zinc is needed only in small amounts, and excessive zinc can be toxic to plants, leading to further issues. Always follow the application rates specified on product labels.
- Regular Monitoring: After treatment, closely monitor the plant for signs of improvement, especially in new growth. Recovery signs include the normalization of leaf size and the disappearance of chlorosis.
Monitoring and Maintenance
After supplementing zinc, improvements in plant health will be most noticeable in new growth, as the symptoms on older leaves are typically irreversible. It’s essential to regularly monitor the plant’s overall health and growth patterns to ensure a successful recovery from zinc deficiency.
Recognizing the critical role zinc plays in plant health and knowing how to address its deficiency can help growers keep their cannabis plants healthy, vigorous, and productive. This understanding is key to maintaining a thriving cannabis garden.

Address Manganese (Mn) Deficiency Solutions
Manganese is an essential micronutrient for cannabis plants, playing crucial roles in photosynthesis, chloroplast formation, and the synthesis of enzymes involved in nitrogen metabolism. It activates several enzymes that are vital for plant growth and development. A manganese deficiency can lead to significant problems, including reduced growth and impaired photosynthetic activity, which can compromise the plant’s overall health and productivity. Ensuring an adequate supply of manganese helps support strong, healthy plants capable of reaching their full potential.
Symptoms of Manganese Deficiency
- Interveinal Chlorosis: Similar to iron deficiency, manganese deficiency often results in interveinal chlorosis, primarily affecting young leaves. The veins stay green while the areas between them turn yellow.
- Necrotic Spots and Brown Patches: In more severe cases, the chlorotic areas may develop small, dark-brown necrotic spots or larger brown patches.
- Reduced Growth Rates: Deficient plants may exhibit stunted growth due to impaired photosynthetic capabilities.
Solutions for Manganese Deficiency
Correcting a manganese deficiency involves adding manganese to the soil or growing medium in a form that the plants can easily uptake.
- Manganese Sulfate:
- One of the most common and effective treatments for manganese deficiency is manganese sulfate. It can be applied directly to the soil or used as a foliar spray for quicker absorption.
- Chelated Manganese:
- Chelated forms of manganese are readily available to plants and can be particularly useful in hydroponic setups or in soil with high pH levels, where manganese availability is reduced.
- Micronutrient Mixes:
- Fertilizers that contain a balanced mix of micronutrients, including manganese, can help prevent deficiencies and ensure overall plant health.
Best Practices
- Soil Testing: Before applying manganese supplements, it’s beneficial to perform a soil test to confirm manganese deficiency and to understand the soil’s overall nutrient profile.
- pH Adjustment: Manganese availability decreases in alkaline soils. Adjusting soil pH to the optimal range for cannabis (6.0 to 7.0 for soil grows) can enhance manganese uptake.
- Application Rate: Follow the recommended application rates for manganese supplements carefully to avoid toxicity, which can occur with excessive manganese.
Monitoring and Maintenance
After correcting a manganese deficiency, keep an eye on your cannabis plants for signs of recovery, particularly in new growth. Look for the disappearance of chlorosis and the return of vibrant green color in young leaves as indicators of successful recovery.
Early identification and treatment of manganese deficiency are key to maintaining the health and productivity of your cannabis plants. Ensuring adequate manganese levels supports strong growth and overall plant development, helping your garden thrive.
Correct Boron (B) Deficiency Tactics
Boron is a critical micronutrient for cannabis plants, playing a key role in cell wall formation and essential processes like cell division, protein synthesis, and the development of new tissues. It helps regulate carbohydrate metabolism and is crucial for the movement of sugars across plant tissues. A boron deficiency can cause major growth issues in cannabis, leading to stunted development and significantly reduced yields.
Symptoms of Boron Deficiency
- New Growth Appears Thick and Twisted: One of the earliest signs of boron deficiency is abnormal growth patterns in new shoots, which may appear thickened and twisted.
- Brittle Plant Tissue: Plants may exhibit brittle growth, with stems and leaves easily breaking.
- Poor Root Development: Root systems may become stunted or malformed, affecting the plant’s ability to uptake water and nutrients.
- Flower and Fruit Development: In severe cases, boron deficiency can impact the development of flowers and seeds, leading to reduced yields.
Solutions for Boron Deficiency
Correcting boron deficiency involves careful supplementation, as boron toxicity can occur with even slight over-application.
- Boron Supplements:
- Soluble boron products, such as borax or boric acid, can be diluted in water and applied to the soil. The concentration should be kept low to avoid toxicity.
- Foliar Spray:
- Applying a boron solution directly to the leaves can provide a quick remedy for deficiency, allowing for direct absorption by the plant.
- Micronutrient Fertilizers:
- Using a balanced micronutrient fertilizer that includes boron can help prevent deficiencies and ensure overall plant health.
Best Practices
- Careful Application: Due to the narrow range between boron deficiency and toxicity, it’s crucial to apply boron supplements carefully, following label instructions closely.
- Soil Testing: Conduct a soil test to confirm boron deficiency. This will help avoid unnecessary or excessive application.
- Monitor pH: Soil pH can affect boron availability, with lower availability at high pH levels. Adjusting soil pH to the optimal range for cannabis (6.0 to 7.0) can improve boron uptake.
Monitoring and Maintenance
After supplementing boron, it’s crucial to monitor your cannabis plants for signs of recovery, particularly in new growth. Recovery is usually gradual, with improvements marked by normalized growth patterns and increased strength and elasticity in plant tissues.
Properly addressing boron deficiency, while being careful to avoid toxicity, is essential for the healthy development and productivity of cannabis plants. Managing boron levels accurately helps maintain balanced nutrition, supporting optimal growth and preventing potential issues. This careful approach ensures your plants can thrive, yielding robust and healthy results.

Correction Best Practices for Nutrient Deficiencies in Cannabis
Correcting nutrient deficiencies in cannabis involves a delicate balance of observation, expertise, and timely action. Here are some best practices to help your plants recover and stay healthy throughout their growth cycle:
- Diagnose Accurately: Begin by carefully identifying the specific nutrient deficiency. Look for symptoms such as discoloration, leaf deformities, or stunted growth, and cross-reference these with known deficiency signs for accurate diagnosis.
- Adjust Nutrient Levels Gradually: When addressing a deficiency, avoid overcorrecting. Gradually adjust the nutrient levels to avoid shocking the plant, which could lead to other issues, like nutrient toxicity.
- Monitor pH Levels: Maintaining the correct soil or hydroponic system pH is crucial, as it affects nutrient availability. Ensure the pH level is within the optimal range for cannabis to facilitate proper nutrient absorption.
- Use Quality Nutrients: Choose high-quality nutrient solutions or supplements designed specifically for cannabis. These products are formulated to provide the necessary elements in balanced proportions.
- Observe New Growth: Recovery is typically visible in new growth rather than existing leaves. Monitor the new leaves for signs of improvement, such as healthy color and structure.
- Maintain Consistent Care: Consistency in watering, lighting, and environmental conditions helps stabilize the plant’s overall health, making it easier to manage nutrient levels.
- Document Changes: Keep a grow journal to track symptoms, interventions, and improvements. This record will help you refine your approach and prevent future deficiencies.
By following these best practices, you can effectively manage nutrient deficiencies in your cannabis plants, ensuring they recover quickly and continue to thrive. This careful approach not only addresses immediate issues but also supports long-term plant health and productivity.
Overview of Nutrient Management in Cannabis Cultivation
Effective nutrient management is crucial for successful cannabis cultivation, as it directly impacts plant growth, health, and the quality of the buds produced. Proper nutrient management involves understanding the specific needs of cannabis plants at different stages of their lifecycle, being able to identify signs of nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, and knowing the appropriate measures to take to correct these issues. Here’s an overview of essential practices for managing nutrients in cannabis cultivation.
1. Understanding Nutrient Needs by Growth Stage
- Seedling Stage: Requires minimal nutrients; focus on gentle feeding to avoid burning young plants.
- Vegetative Stage: High demand for nitrogen to support leaf and stem growth.
- Flowering Stage: Increased need for phosphorus and potassium to promote bud development and overall plant health.
2. Monitoring and Adjusting pH Levels
- Soil Cultivation: Maintain pH levels between 6.0 and 7.0 to ensure optimal nutrient availability.
- Hydroponic Systems: Keep pH levels between 5.5 and 6.5 for proper nutrient uptake.
3. Recognizing Nutrient Deficiencies and Toxicities
- Deficiencies: Look for symptoms like yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or leaf spots. Each deficiency presents specific signs, such as nitrogen deficiency causing overall yellowing or magnesium deficiency leading to interveinal chlorosis.
- Toxicities: Symptoms include nutrient burn (browning leaf tips), unusual leaf colors, or slowed growth. Overfeeding or incorrect pH can cause toxic buildup.
4. Using Quality Nutrients
- Choose nutrient products specifically formulated for cannabis, which provide balanced nutrition tailored to the plant’s needs. Organic or synthetic options are available, each with unique benefits.
5. Regular Monitoring and Adjustments
- Conduct regular checks on your plant’s health, growth rate, and leaf color. Adjust nutrient levels and pH based on observed changes and growth stages.
6. Consistent Watering Practices
- Maintain a consistent watering schedule to prevent nutrient lockout, which occurs when nutrients become unavailable to the plant due to irregular watering or improper pH.
7. Implementing a Feeding Schedule
- Develop a feeding schedule that aligns with the growth stages of the plant, gradually increasing or decreasing nutrient levels as needed. Flush the plants occasionally to prevent salt buildup, especially in hydroponic systems.
8. Keeping a Grow Journal
- Document your nutrient management practices, including nutrient types, quantities, pH levels, and any observed plant responses. This record helps in refining your approach and troubleshooting issues for future grows.
By adhering to these essential practices, cannabis growers can manage nutrients effectively, ensuring vigorous growth and maximizing the potential for high-quality yields. Proper nutrient management not only addresses immediate plant health but also sets the foundation for a successful and productive cultivation experience.to adjust practices based on plant responses. By mastering these aspects, cultivators can ensure their cannabis plants are healthy, vibrant, and productive.
Watch Your Grows Close
Understanding and correcting cannabis plant deficiencies is a crucial aspect of successful cultivation. The ability to accurately identify and address these deficiencies can be the difference between a mediocre harvest and a bountiful, potent yield. Armed with the knowledge of essential nutrients, their functions, and how to replenish them, growers can tackle most challenges that come their way. Remember, the key to healthy cannabis plants lies not only in recognizing the signs of deficiency but also in preventing them through proactive nutrient management and care. As you refine your cultivation practices, you’ll find that addressing nutrient deficiencies becomes an intuitive part of your gardening routine, ensuring that your cannabis plants remain vibrant and productive season after season.
To further enhance your cultivation skills and broaden your understanding of cannabis, it’s important to explore the different strains and their unique characteristics. For a deeper dive into the world of cannabis varieties, check out our comprehensive guide on Cannabis Sativa, Hybrid, and Indica. This resource will help you understand the distinct traits and effects of these popular strains, enabling you to make informed choices for your garden.
Additional Resources:
- Grow That Sh!t Better by Maximus Reigns – An essential eBook for both novice and experienced growers, offering advanced techniques and tips for improving cannabis cultivation.
- Cannabis Growers’ Handbook by Ed Rosenthal – A comprehensive guide that covers all aspects of growing cannabis, from setup to harvest.
- Royal Queen Seeds Blog – A rich resource for growers, featuring articles on growing techniques, strain information, and more.
- Need Cannabis Seeds? – Seedsman Seeds has a variety of seeds for all growers from new and seasoned to medical and CBD users.
- Grow Weed Easy – A website dedicated to providing step-by-step guides and resources for growing cannabis at home.
These resources will provide you with valuable insights and practical tips to take your cannabis cultivation to the next level. By continuously expanding your knowledge and refining your techniques, you can ensure a successful and rewarding growing experience.